A Single Qubit Approach for Binary Classification
Learn how to implement a classification model using a single qubit encoding method.
The utilization of a single qubit for machine learning methodologies is a prominent strategy among scholars and professionals in the field of quantum machine learning (QML). This approach is particularly highlighted by the influential work of Pérez-Salinas et al. in their paper, "Data re-uploading for a universal quantum classifier."
In this discussion, we will guide you through the implementation of a single qubit using the Python library sQUlearn. sQUlearn offers high-level interfaces that are compatible with scikit-learn, accommodating various kernel methods and Quantum Neural Networks (QNNs). These interfaces harness the underlying functionalities of both the QNN engine and the quantum kernel engine. An executor is utilized to facilitate experiments on both simulated and real hardware platforms within the Qiskit framework.
The forthcoming sections presume that your data has been effectively prepared and is ready to be encoded in subsequent steps. Should this not be the case, we recommend consulting the following article from our blog:
Dimensionality Reduction for Quantum Machine Learning: Integrating LDA and K-Means
In Quantum Machine Learning (QML), the preparation of data is a crucial step that often determines the effectiveness and efficiency of the algorithms used. One of the key challenges in this process is dimensionality reduction, which involves transforming high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional space. This is particularly important in quantum comp…
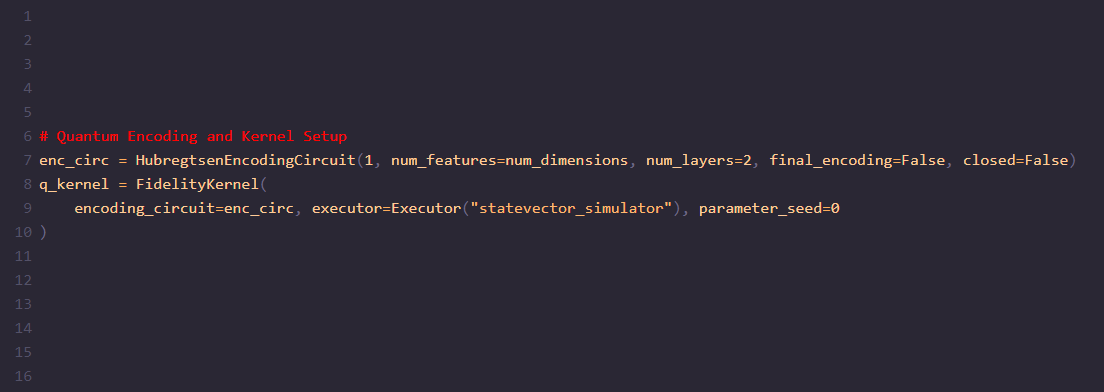
Quantum Encoding and Kernel Setup
Import Quantum Modules and Setup Encoding
from squlearn.encoding_circuit import HubregtsenEncodingCircuit
from squlearn.kernel import FidelityKernel
from squlearn.util import Executor
enc_circ = HubregtsenEncodingCircuit(1, num_features=num_dimensions, num_layers=2, final_encoding=False, closed=False)
q_kernel = FidelityKernel(
encoding_circuit=enc_circ, executor=Executor("statevector_simulator"), parameter_seed=0
)Purpose: To establish the quantum encoding circuit and quantum kernel for processing data.
How It Works:
Encoding Circuit:
HubregtsenEncodingCircuitis used to prepare quantum states based on classical data features. This encoding method creates the data re-uploading circuit as presented in "Training Quantum Embedding Kernels on Near-Term Quantum Computers" by Hubregsten et al. The configuration specifies the circuit to operate with 1 qubit, a number of features based onnum_dimensions(could be the number you decide considering the dataset and dimensionality reduction applied), and composed through 2 layers.Quantum Kernel:
FidelityKernelcomputes the kernel matrix used in the quantum SVC (QSVC). It uses the defined encoding circuit (enc_circ) and an executor that runs the circuit using a statevector simulator.
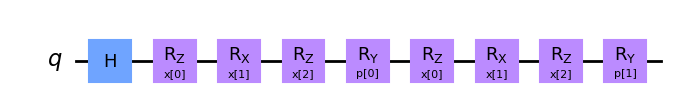
Draw the Circuit
enc_circ.draw('mpl', style='clifford')Purpose: To visualize the quantum circuit used for data encoding.
How It Works: Calls the
drawmethod on theenc_circobject to render the circuit using Matplotlib with a specified style, providing a visual representation of the quantum operations.
Quantum Support Vector Classifier Setup
Initialize and Configure QSVC
from squlearn.kernel import QSVC
qsvc = QSVC(
quantum_kernel=q_kernel,
C=0.05,
probability=True,
random_state=0
)Purpose: To initialize the quantum support vector machine with a quantum kernel.
How It Works:
Constructs a QSVC instance using the
FidelityKernelpreviously defined. The QSVC is configured with a regularization parameterCof 0.05, enabling probability estimates (probability=True), and setting a seed for random operations to ensure reproducibility. C paramenter should be adjusted to match the best performance of your model.
Train the QSVC Model
qsvc.fit(X_train, y_train)Purpose: To train the quantum support vector classifier on the preprocessed and encoded training data.
How It Works: The
fitmethod adjusts the model parameters to minimize the loss function, effectively learning from the training dataX_trainwith corresponding labelsy_train.
Model Evaluation Using ROC AUC
Make Predictions and Evaluate
predictions_qsvc = qsvc.predict_proba(X_test_qsvc)[:,1]
auc_test = roc_auc_score(y_test, predictions_qsvc)
print("AUC for the test set: ", auc_test)Purpose: To evaluate the performance of the QSVC model using the Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve (AUC).
How It Works:
Predictions: Uses the
predict_probamethod of QSVC to get predicted probabilities for the positive class from the test setX_test_qsvc.AUC Calculation: The
roc_auc_scorefunction calculates the AUC, which measures the model's ability to distinguish between classes.The AUC score is then printed, providing a quantitative measure of model performance on the test set.